Cracked Tooth Treatment
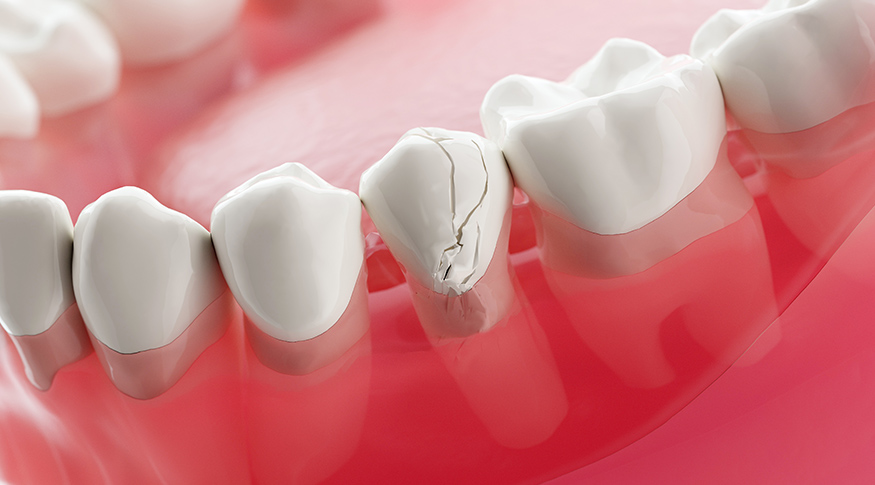
Cracked tooth syndrome (CTS) is a dental condition characterized by the presence of an incomplete fracture within a tooth, often too small to be detected on standard radiographs but significant enough to cause intermittent discomfort.
Clinical Features
- Patients typically report sharp, transient pain upon biting or with thermal stimuli, which may be difficult to localize.
- The crack may involve enamel, dentin, and potentially extend toward the pulp.
- Common etiologies include occlusal trauma from bruxism, structurally compromised teeth with large restorations, direct trauma, or biting on hard substances.
- Diagnosis often requires specialized techniques such as bite tests, magnification, or transillumination.
- Management depends on the extent and location of the crack and may include direct restoration, full-coverage crown, endodontic therapy, or extraction in severe cases.
Purpose
It is a clinically challenging condition that requires early detection and intervention to preserve tooth structure and function.



